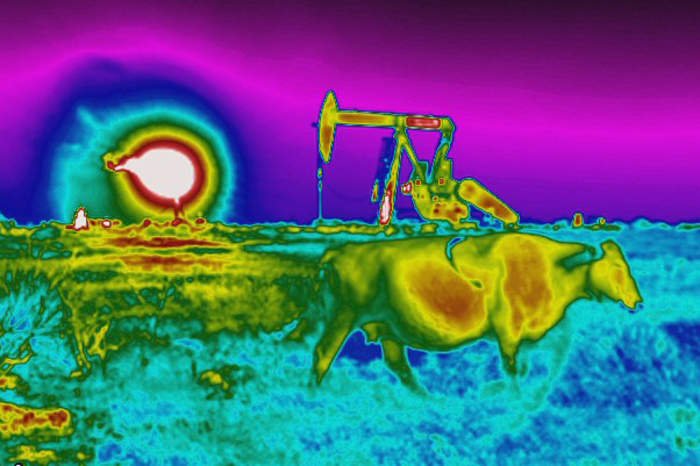
The blob on the satellite tv for pc picture is a rainbow of colours. An analyst digitally sharpens it and there, highlighted in crimson, is the supply: a concrete oil pad spewing methane.
Within the 75,000-square-mile (194-square-kilometer) Permian Basin straddling Texas and New Mexico, the most efficient oil and gasoline area on the earth, large quantities of the highly effective greenhouse gasoline escape from wells, compressor stations and different tools.
Most efforts to cut back emissions have centered on so-called “tremendous emitters” just like the one within the satellite tv for pc picture, that are comparatively simple to search out with bettering satellite tv for pc imaging and different aerial sensing.
Now researchers say a lot smaller sources are collectively answerable for about 72% of methane emissions from oil and gasoline fields all through the contiguous U.S. These have usually gone undetected.
“It is actually (vital to) strategy the issue from each ends as a result of the high-emitting tremendous emitters are vital, however so are the smaller ones,” stated James Williams, a post-doctoral science fellow on the Environmental Protection Fund and lead creator on a brand new research that took a complete have a look at emissions throughout the nation’s oil and gasoline basins.
Addressing methane is vital as a result of it accounts for about one third of all greenhouse gasoline emissions that contribute to local weather change.
Tackling methane emissions within the Permian is very difficult as a result of there are greater than 130,000 energetic nicely websites owned by everybody from household operators to worldwide conglomerates, consultants stated. Every web site can have a number of oil wells.
“The Permian is in some ways probably the most sophisticated basin on the earth; it’s extremely dense there … with huge, small and all the pieces in between,” stated Steve Hamburg, chief scientist on the Environmental Defense Fund.
What’s extra, pipelines, processing and different actions usually are owned by completely different corporations — with tens of 1000’s of factors the place methane would possibly escape, both via leaks or intentional venting.
An Israeli firm that used satellite tv for pc information and synthetic intelligence to search for leaks in Midland County, Texas, the center of the Permian Basin, discovered 50 separate plumes emanating from 16 of 30 websites it monitored. Most have been bleeding over 4,500 kilograms of dangerous gasoline per hour and 5 exceeded 10,000, far above the Environmental Safety Company’s tremendous emitter threshold of 100 kg/hr.
However the largest shock, “was seeing a number of small emissions on this very crowded place … so shut to one another, so near an space the place folks really dwell,” stated Omer Shenhar, vice chairman of product at Momentick, which offers satellite-based monitoring to grease and gasoline corporations.
Methane traps over 80 occasions extra warmth near the Earth than carbon dioxide does, ton for ton. What’s extra, concentrations have virtually tripled since pre-industrial occasions.
A strong new satellite tv for pc known as MethaneSAT that launched this yr will have the ability to detect small emissions over vast areas that different satellites cannot. Researchers will even have the ability to observe methane over time in all of the world’s main oil-producing basins.
“We have by no means had that,” stated the EDF’s Hamburg, who leads the venture.
Though the satellite tv for pc can’t pinpoint these smaller sources, “you needn’t” as a result of operators on the bottom can discover the sources, Hamburg stated.
Within the U.S., oil and gasoline corporations can be required to routinely search for leaks at new and current websites, together with from wells, manufacturing amenities and compressor station underneath a brand new EPA rule.
The rule additionally phases out the apply of routinely burning off extra methane, known as flaring, and requires upgrading gadgets that leak methane.
States have till 2026 to develop a plan to implement that rule for current sources.
Oil and pure gasoline corporations additionally must pay a federal fee per ton of leaked methane above a sure degree underneath a ultimate rule introduced final month by the Biden administration, though the incoming Trump administration might get rid of that.
Methane — the first part of pure gasoline — is efficacious commercially, but many operators within the Permian regard it as a nuisance byproduct of oil manufacturing and flare it as a result of they have not constructed pipelines to hold it to market, Duren and Hamburg stated.
Neither the Permian Basin Petroleum Affiliation nor the U.S. Oil & Gasoline Affiliation responded to requests for remark.
Riley Duren, CEO of the nonprofit Carbon Mapper, who was not concerned within the research, stated it is at all times vital to sort out tremendous emitters as a result of they’ve such an outsize impression. They’re usually fleeting however not at all times. Some proceed for weeks, months or years.
Every little thing provides up.
“I feel … what proportion of the overall comes from a lot of small sources versus tremendous emitters is much less vital than what do you do with the knowledge,” stated Duren. There are “actually 1000’s and 1000’s of items of kit they usually can blow a leak at any time.”
___
The Related Press’ local weather and environmental protection receives monetary assist from a number of non-public foundations. AP is solely answerable for all content material. Discover AP’s standards for working with philanthropies, an inventory of supporters and funded protection areas at AP.org.
Copyright 2024 The Related Press. All rights reserved. This materials is probably not printed, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed with out permission.